New Spectroscopy Method Simplifies Measurement of Microplastics in Soil
새로운 분광학 방법으로 토양 내 미세플라스틱 측정을 단순화
Researchers devised novel method to measure microplastic concentrations in soil using spectroscopy at two wavelengths.
연구자들은 두 가지 파장의 분광학을 사용하여 토양의 미세플라스틱 농도를 측정하는 새로운 방법을 고안했습니다.
News
Published: June 17, 2024

Read time: 2 minutes
Current techniques for measuring nano/microplastic (N/MP) concentrations in soil require the soil organic matter content to be separated and have limited resolution for analyzing N/MPs sized <1 µm. Therefore, researchers have developed a novel yet simple method to measure N/MP concentration in different soil types using spectroscopy at two wavelengths. This method does not require the soil to be separated in order to detect the N/MPs and can accurately quantify N/MPs regardless of their size.
토양 내 #나노/미세플라스틱 (#N/MP ) 농도를 측정하기 위한 현재 기술에서는 토양 유기물 함량을 분리해야 하며 <1 µm 크기의 N/MP를 분석하기 위한 분해능이 제한되어 있습니다. 따라서 연구자들은 두 가지 파장의 분광학을 사용하여 다양한 토양 유형에서 N/MP 농도를 측정하는 새롭고 간단한 방법을 개발했습니다. 이 방법은 N/MP를 검출하기 위해 토양을 분리할 필요가 없으며 크기에 관계없이 N/MP를 정확하게 정량화할 수 있습니다.
Nano and microplastics are a well-known menace, found practically everywhere in nature, including soil, oceans, drinking water, air, and even the human body. Studies show that soils in particular hold a significant portion of N/MPs. The problem with these N/MPs is their microscopic size, which allows them to easily migrate through soil into the ground or freshwater bodies due to rainwater leaching. From there, they enter the human body. Hence, it is imperative to understand the distribution and movement of the soil’s N/MPs to gauge their threat and mitigate it.
나노 및 미세플라스틱은 토양, 바다, 식수, 공기, 심지어 인체까지 포함하여 자연의 거의 모든 곳에서 발견되는 잘 알려진 위협입니다. 연구에 따르면 토양은 특히 N/MP의 상당 부분을 차지합니다. 이러한 N/MP의 문제점은 미세한 크기로 인해 빗물 침출로 인해 토양을 통해 지하수 또는 담수체로 쉽게 이동할 수 있다는 점입니다. 거기에서 그들은 인체에 들어갑니다. 따라서 위협을 측정하고 완화하려면 토양의 N/MP의 분포와 이동을 이해하는 것이 중요합니다.
Current techniques for measuring N/MP concentrations in soil require separating the soil organic matter content through chemical and physical processes. Subsequently, the isolated N/MPs are analyzed using a microscope, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, Pyrolysis–gas chromatography/mass spectrometry, or Raman spectrometry. However, these techniques require advanced skills and have limited resolution for analyzing N/MPs smaller than 1 µm. Moreover, often some of the N/MPs in the soil are lost during the separation process, leading to inaccurate measurements. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a simple yet accurate method to detect and measure N/MPs ≤1 µm in soil.
토양의 N/MP 농도를 측정하기 위한 현재 기술에서는 화학적 및 물리적 공정을 통해 토양 유기물 함량을 분리해야 합니다. 이어서, 분리된 N/MP는 현미경, #푸리에변환적외선분광법 , #열분해가스크로마토그래피/질량분석법 또는 #라만분광법 을 사용하여 분석됩니다. 그러나 이러한 기술에는 고급 기술이 필요하며 1μm보다 작은 N/MP를 분석하기 위한 분해능이 제한되어 있습니다. 게다가 분리 과정에서 토양의 N/MP 중 일부가 손실되어 측정이 부정확해지는 경우가 많습니다. 따라서 토양에서 N/MPs 1μm 이하를 감지하고 측정하기 위한 간단하면서도 정확한 방법을 개발하는 것이 필요합니다.
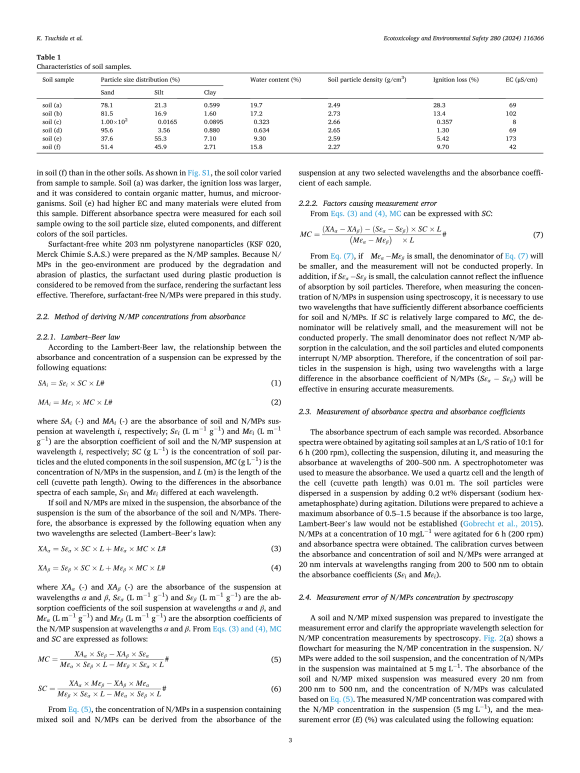
To this end, a team of researchers led by Mr. Kyouhei Tsuchida from Waseda University and National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, along with Dr. Yukari Imoto, Dr. Takeshi Saito, and Dr. Junko Hara from the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology and Dr. Yoshishige Kawabe, also from Waseda University, devised a novel and simple method to measure N/MP concentrations in soil using spectroscopy without separating the soil organic matter. Spectroscopy can determine the concentration of N/MPs in soils based on how much light of a particular wavelength passes through the sample and how much gets absorbed. In this way, spectroscopy can potentially detect N/MPs regardless of size, provided the correct wavelengths are used to distinguish between the N/MPs and soil. Accordingly, the researchers developed a method to use the difference between the absorbance spectra of N/MPs and soil particles to quantify the N/MPs. Their findings were published in Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety journal on 28 May 2024.
이를 위해 와세다 대학의 쓰치다 쿄헤이(Tsuchida Kyouhei) 국립산업기술종합연구소 연구원과 국립 고등연구소의 이모토 유카리 박사, 사이토 다케시 박사, 하라 준코 박사가 이끄는 연구진이 팀을 구성했습니다. 산업 과학 기술 및 와세다 대학의 Yoshishige Kawabe 박사는 토양 유기물을 분리하지 않고 분광학을 사용하여 토양의 N/MP 농도를 측정하는 새롭고 간단한 방법을 고안했습니다. 분광학은 특정 파장의 빛이 샘플을 통과하는 양과 흡수되는 양을 기준으로 토양의 N/MP 농도를 결정할 수 있습니다. 이러한 방식으로 분광학은 N/MP와 토양을 구별하기 위해 올바른 파장을 사용하는 경우 크기에 관계없이 잠재적으로 N/MP를 감지할 수 있습니다. 이에 따라 연구진은 N/MP를 정량화하기 위해 N/MP와 토양 입자의 흡광 스펙트럼 차이를 이용하는 방법을 개발했습니다. 그들의 연구 결과는 2024년 5월 28일 생태독성학 및 환경 안전 저널에 게재되었습니다.
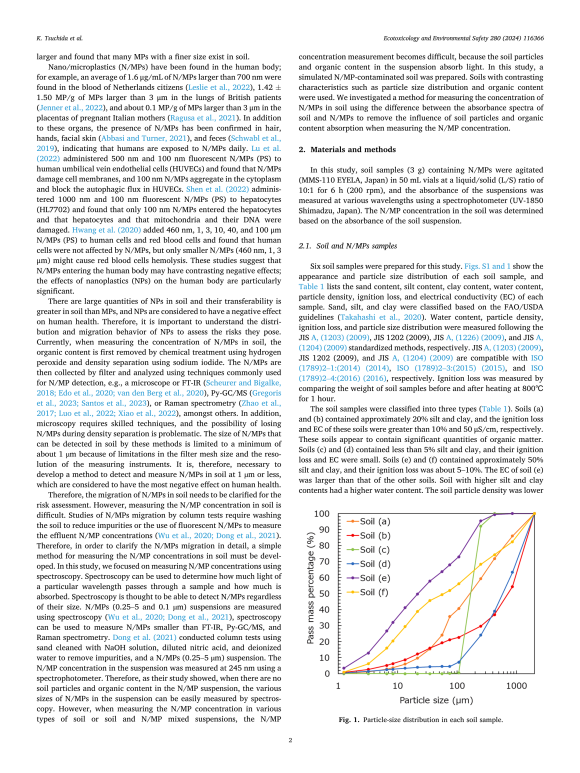
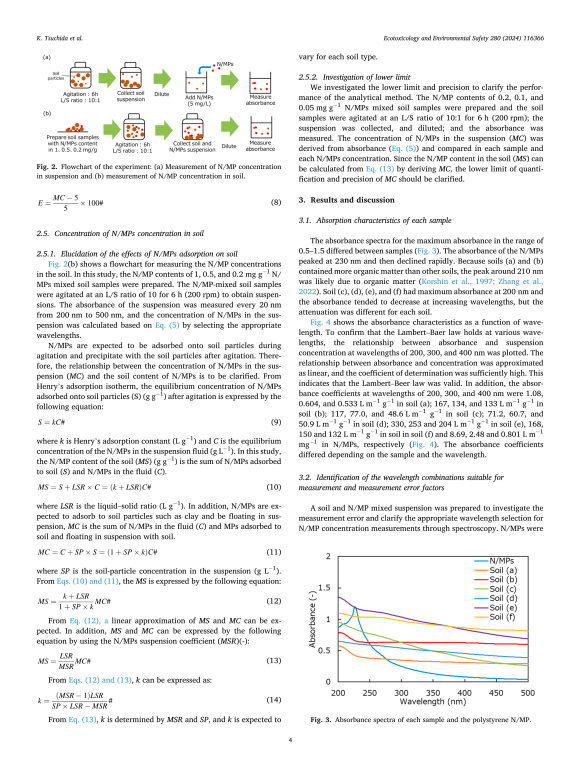
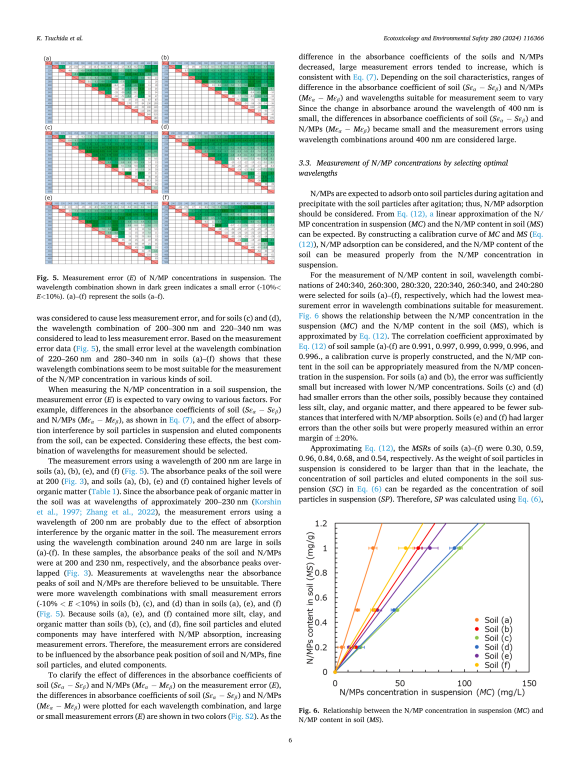
Six soil suspensions were created from soil samples with different characteristics, such as particle size distribution and organic content, and were mixed with polystyrene nanoparticles sized 203 nm. This created six different simulated N/MP-contaminated soil suspensions, with the N/MP concentration maintained at 5 mg/L. “We measured the absorbance of these soil suspensions at various wavelengths ranging from 200 to 500 nm using a spectrophotometer and based on this, determined the N/MP concentrations in the soil. Then the best combination of two wavelengths was identified for measuring N/MPs, which helped negate the interference from soil particles and leached components in the suspension,” explains Tsuchida.
입자 크기 분포, 유기물 함량 등 서로 다른 특성을 지닌 토양 시료로부터 6개의 토양 현탁액을 생성하고 203 nm 크기의 폴리스티렌 나노입자와 혼합했습니다. 이를 통해 N/MP 농도가 5 mg/L로 유지되는 6개의 서로 다른 시뮬레이션 N/MP 오염 토양 현탁액이 생성되었습니다. “우리는 분광 광도계를 사용하여 200~500 nm 범위의 다양한 파장에서 이러한 토양 현탁액의 흡광도를 측정하고 이를 기반으로 토양의 N/MP 농도를 결정했습니다. 그런 다음 N/MP 측정을 위해 두 파장의 가장 좋은 조합이 식별되었으며, 이는 현탁액에서 토양 입자와 침출된 구성 요소의 간섭을 무효화하는 데 도움이 되었습니다.”라고 Tsuchida는 설명합니다.
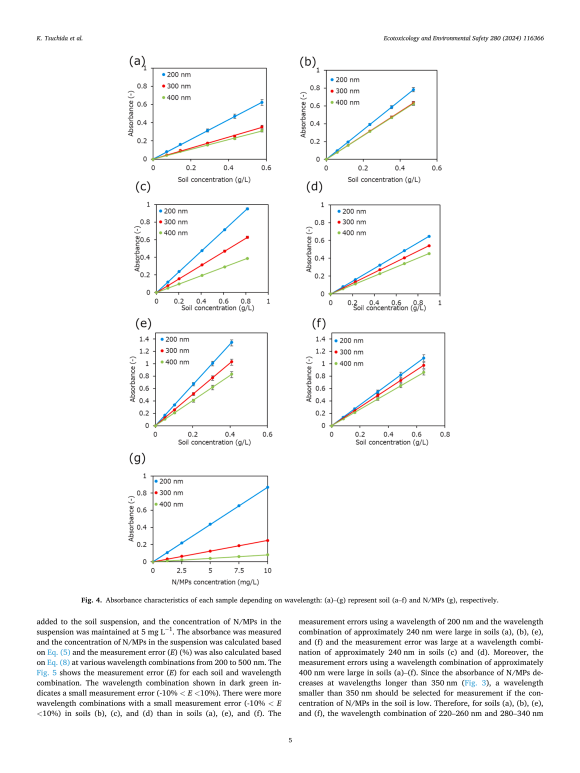
The researchers found that a wavelength combination of 220–260 nm and 280–340 nm had the lowest error level for the six samples and was thus found to be suitable for measuring N/MP concentrations in different soil types. They also created a calibration curve between the concentration of N/MPs in the soil suspensions and N/MP content added to the dry soil samples. The calibration curve showed a linear relationship between the two variables and took into account the adsorption of N/MPs on soil particles. This enabled accurate estimation of the concentration of N/MPs in the soil.
연구진은 220~260 nm와 280~340 nm의 파장 조합이 6개 샘플에 대해 가장 낮은 오류 수준을 가지며 따라서 다양한 토양 유형에서 N/MP 농도를 측정하는 데 적합한 것으로 밝혀졌습니다. 그들은 또한 토양 현탁액의 N/MP 농도와 건조한 토양 샘플에 첨가된 N/MP 함량 사이의 보정 곡선을 만들었습니다. 보정 곡선은 두 변수 사이의 선형 관계를 보여주었으며 토양 입자에 대한 N/MP의 흡착을 고려했습니다. 이를 통해 토양의 N/MP 농도를 정확하게 추정할 수 있었습니다.
These results demonstrate the efficacy of this simple spectroscopy-based method to correctly measure the concentration of N/MPs in soil, without any cumbersome separation process. “Our novel measurement approach can quantify different N/MPs, including polyethylene and polyethylene terephthalate, in a variety of soils and can easily be used as an initial assessment tool. Moreover, it can help further our understanding of the distribution and migration behavior of N/MPs in the geosphere environment,” concludes Tsuchida.
이러한 결과는 번거로운 분리 과정 없이 토양 내 N/MP 농도를 정확하게 측정할 수 있는 간단한 분광학 기반 방법의 효능을 입증합니다. “우리의 새로운 측정 접근 방식은 다양한 토양에서 폴리에틸렌 및 폴리에틸렌 테레프탈레이트를 포함한 다양한 N/MP를 정량화할 수 있으며 초기 평가 도구로 쉽게 사용할 수 있습니다. 또한 이는 지구권 환경에서 N/MP의 분포 및 이동 동작을 더 깊이 이해하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.”라고 Tsuchida는 결론지었습니다.
Reference: Tsuchida K, Imoto Y, Saito T, Hara J, Kawabe Y. A novel and simple method for measuring nano/microplastic concentrations in soil using UV-Vis spectroscopy with optimal wavelength selection. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety. 2024:116366. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116366
최적의 파장 선택이 가능한 UV-Vis 분광법을 사용하여 토양의 나노/미세 플라스틱 농도를 측정하는 새롭고 간단한 방법




******************************************************************************************************
#미세플라스틱 #시험분석 기술서비스 #시험표준개발 #국제공인시험기관 #KOLAS
#시험/분석 #환경 #수질 #토양 #대기 #폐기물 #타이어 #슬러지
#식품 #음료 #벌꿀 #주류 #소금 #어패류 #해조류 #미세플라스틱분석 #미세플라스틱시험
#세탁폐수 #미세섬유 #세탁망 #필터 #화장품 #치약 #생활화학제품 #세탁기필터
#식품용기 #티백 #젖병 #종이컵 #정수기 #NSF 평가 #젖병소독기
#표준개발 ISO/TC61/SC14, TC38, TC147/SC2&SC6 (Microplastics) Korean Delegate
IEC/TC 111/WG 3 & JWG 14 Co-Convenor
IEC 62321-3-2(#Halogen ),-10 (#PAHs ), -13(#BPA ), -14(#SCCP/MCCP ) Project leader
- 분석장비: #TEDGCMS, #microFT-IR #microRaman, #ICPMS #XRF #Combustion-IC 등
#PAHs분석 #SCCP/MCCP분석 #Halogen분석 #PAHs #SCCP #MCCP #halogen #PFAS
#생체시료분석 #생체미세플라스틱분석 #혈액미세플라스틱분석 #인체미세플라스틱분석
#생체시료시험 #생체미세플라스틱시험 #혈액미세플라스틱시험 #혈액미세플라스틱검사
#미세플라스틱RM #미세플라스틱표준시료 #미세플라스틱표준물질 #태블릭RM
#ISO/IEC17025 ( #국제공인시험기관 , #KOLAS ) 인정 연구소
******************************************************************************************************